Table to compare acid-base theories.
The following table shows the different acid-base theories:
Acid-base theory |
Definition of acid |
Example of acid |
Definition of base |
Example of base |
|---|---|---|---|---|
Arrhenius |
A species that increases the concentration of hydrogen ions, H⁺, in an aqueous solution. The H⁺ ions react immediately with the H₂O to form oxidanium ions (H₃O⁺). |
HCl(ac)→H+(ac)+Cl-(ac) |
A species that increases the concentration of hydroxide ions, OH-, in an aqueous solution. |
NaOH(ac)→Na+(ac)→OH – (ac) |
Brønsted-Lowry |
Proton-donating species, H⁺. *Water is defined as an amphoteric substance since it can act as an acid or a base. *Conjugated acid is the species formed when a Brønsted-Lowry base accepts a proton. |
NH3(g)+HCl(g) →NH4Cl(s) * It is also expressed as 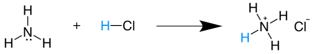 * Conjugated acid 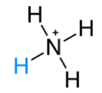 |
A species that accepts a proton, which requires a lone pair of electrons to bond to H+. *Conjugate base is the species formed after a Brønsted-Lowry acid gives up a proton. |
NH3(ac)+H2O(l⇌NH4+(ac)+OH-(ac) *Conjugate base OH-(ac) |
Lewis |
Species that accepts and shares a pair of electrons yielded by a base. |
Acid + Base → adduct H++ :NH3 |
A species that gives up a pair of electrons and shares them with an acid. |
Acid + Base → adduct 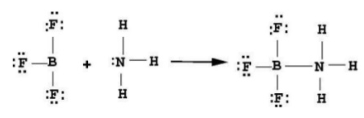 |
Examples of acid-base reactions according to different theories.
Reaction |
Arrhenius |
Brønsted-Lowry |
Lewis |
Comment |
|---|---|---|---|---|
HCl + NaOH → NaCl +H2O |
Acid + Base → Salt + Water
HCl + NaOH → NaCl +H2O |
Acid + Base → Base conj. + Acid conj.
HCl + NaOH → NaCl + H2O |
Acid + Base → adduct
HCl + NaOH → NaCl +H2O |
|
H2PO4-+ HCl → H3PO4 + Cl- |
Not applicable |
Acid + Base → Acid conj. + Base conj.
H2PO4- + HCl → H3PO4 + Cl- |
Acid + Base → adduct
H2PO4- + HCl → H3PO4 + Cl- |
* The Arrhenius theory does not apply because an OH ion is necessary for the definition. |
AlCl3 + NH3 → [Al(NH3)Cl3]. |
Not Applicable |
Not applicable |
Acid + Base → adduct
AlCl3 + NH3 → [Al(NH3)Cl3]. |
* All Brønsted-Lowry acids and bases are Lewis acids and bases, but not all Lewis acids and bases are Brønsted-Lowry acids and bases. |
Find more articles here: https://carbotecnia.info/aprendizaje/







