Disinfection with UV light.
The chemical agents used for water disinfection are not the only methods that exist for the inactivation of microorganisms, this can also be achieved through heat and electromagnetic radiation. Heat is used to disinfect beverages by the process of pasteurization. Electromagnetic radiation, specifically gamma radiation is used in the disinfection of some foods and UV radiation in the disinfection of air, water and medical surfaces. Of these two types of radiation only UV has found a place in water treatment applications.
Ultraviolet (UV) light is the name used to describe electromagnetic radiation with wavelengths between 100 – 400 nm (Figure 1 shows the electromagnetic spectrum). The UV spectrum is also subdivided into the following four segments, vacuum UV, short wave UV (UV-C), medium wave UV (UV-B) and long wave UV (UV-A).
These are described below:
- UV-A and UV-B activate melanocytes in the skin to produce melanin (“tanning”).
- UV-B radiation causes sunburn.
- UV-C radiation is the radiation absorbed by DNA and is the most likely cause of skin cancer.
Fig 1. Location of the ultraviolet region in the electromagnetic spectrum.
Equipment configuration.
UV disinfection systems (Figure 2) generally consist of:
- UV lamps (bulbs).
- Transparent quartz sleeves surrounding the bulb, this protects the bulbs from the water.
- The structure that supports the lamps and sleeves in place.
- The power sources.
- In some models the UV dose intensity monitoring sensor.
- Some models include a cleaning system that keeps the quartz sleeves transparent.
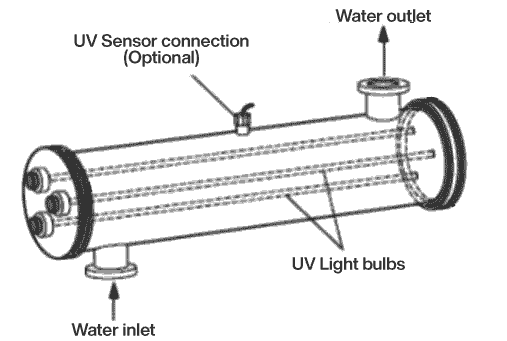
Fig 2. Basic configuration of a UV System
Inactivation mechanisms.
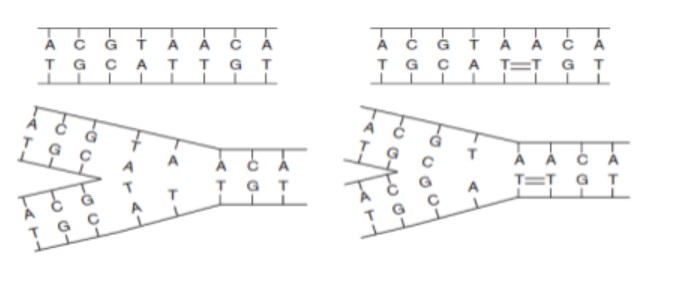
Photons emitted by UV lamps react directly with the nucleic acids of a given organism. These damage the DNA by the dimerization of adjacent Thymine molecules, inhibiting the transcription of the genome (Figure 3). This reaction is not fatal for the microorganism, but it does prevent its successful reproduction.
Fig 3. Thymine dimer formation by UV light interference
What elements prevent the correct operation of UV equipment?
The quality of the water to be treated has an important influence on the performance of UV disinfection systems. The two factors that have the greatest impact on water are dissolved and suspended substances.
- Dissolved substances: There are certain substances dissolved in water that absorb UV radiation and prevent light from passing through the water. The contaminants dissolved in water that present this phenomenon are iron, nitrates and organic matter. Chlorine, hydrogen peroxide and ozone also have important effects on the absorption of UV radiation.
- Suspended substances (particles): Particles suspended in water interfere with the transmission of UV light, this occurs by two mechanisms shown in the figure below:
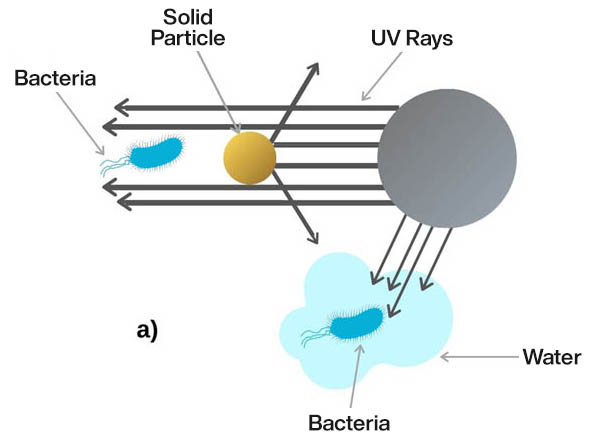
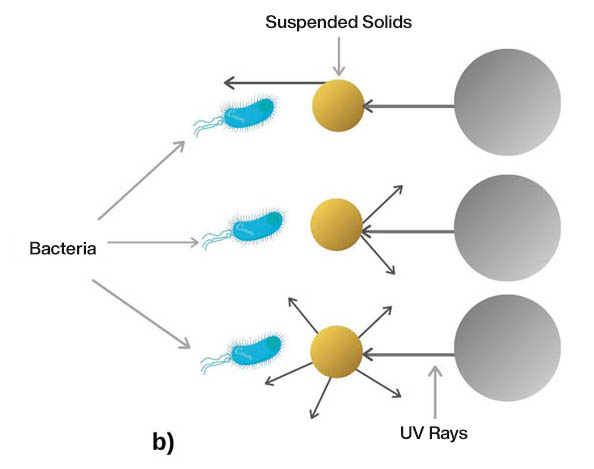
Fig 4. Illustration of particle interference mechanisms.
Find UV products here: https://www.filtrashop.com/?s=luz+uv&post_type=product
Si cuenta con algún proyecto en el que necesite asesoría respecto a la desinfección de agua o equipos ultravioleta escríbanos al correo [email protected] o envíenos un mensaje en el siguiente link: Solicitar más información.