Description
Purofine anionic resin PFA400 and PFA400MB
Advantages of Purofine resins
Purofine PFA400MB:
- It is ideal for demineralization and mixed bed applications, offering high operational capacity and good resistance to organic contamination. Uniform sphere size ensures consistent performance.
Purofine PFA400:
- In addition to sharing the advantages of high operating capacity and good resistance to organic contamination with PFA400MB, this resin is specifically recommended for industrial demineralization applications. It stands out for its more efficient regeneration and has Halal and Kosher certifications, making it suitable for a wide range of applications in different industries.
Comparison table between PFA400 and PFA400MB resins
Feature |
Purofine® PFA400MB |
Purofine® PFA400 |
|---|---|---|
Polymer Structure |
Cross-linked polystyrene gel with divinylbenzene |
Cross-linked polystyrene gel with divinylbenzene |
Appearance |
Spheres |
Spheres |
Functional Group |
Quaternary ammonium type I |
Quaternary ammonium type I |
Ionic Form |
Cl- form |
Cl- form |
Total Capacity (min.) |
1.3 EQ/L (28.4 Kgr/ft³) |
1.3 EQ/L (28.4 Kgr/ft³) |
Moisture Retention |
48 – 54 % |
48 – 54 % |
Average Diameter |
570 ± 50 µm |
570 ± 50 µm |
Coefficient of Uniformity |
1.1 – 1.2 |
1.1 – 1.2 |
Reversible swelling, Cl- → OH- (max.) |
30 % |
30 % |
Specific Density |
1.08 |
1.08 |
Shipping Weight (approx.) |
650 – 700 g/L (40.6 – 43.8 lb/ft³) |
650 – 700 g/L (40.6 – 43.8 lb/ft³) |
Temperature Limit (Cl- form) |
100 °C (212.0 °F) |
100 °C (212.0 °F) |
Temperature Limit (OH- form) |
60 °C (140.0 °F) |
60 °C (140.0 °F) |
Main Applications |
Demineralization, Mixed bed anionic component |
Demineralization – Industrial |
Certifications |
Not specified |
IFANCA Halal Certificate, Kosher Certificate |
Hydraulic Characteristics of Purolite Purofine PFA400MB and Purofine PFA400
The hydraulic characteristics of Purofine® PFA400MB and Purofine® PFA400 resins, including pressure drop and backflushing, are crucial to understanding their performance in practical applications.
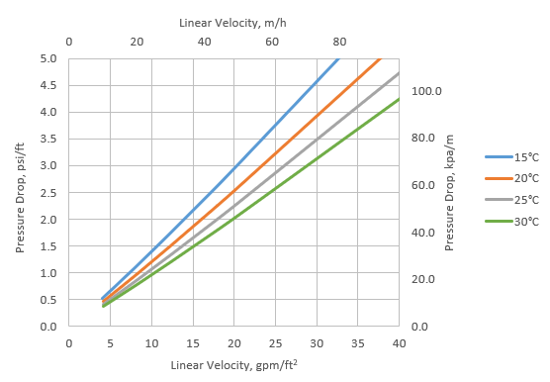
Pressure drop:
- For both Purofine® PFA400MB and Purofine® PFA400, the pressure drop across a well-sorted bed of ion exchange resin depends on several factors, including particle size distribution, bed height, and voids between the exchange material. In addition, the flow rate and viscosity of the solution also play an important role. Factors such as the presence of retained particles in the bed, abnormal compressibility of the resin, or incomplete bed classification can increase pressure loss. Service flows can vary from 10 to 40 bed volumes per hour, depending on the quality of the water to be treated, the specific application, and the plant design.
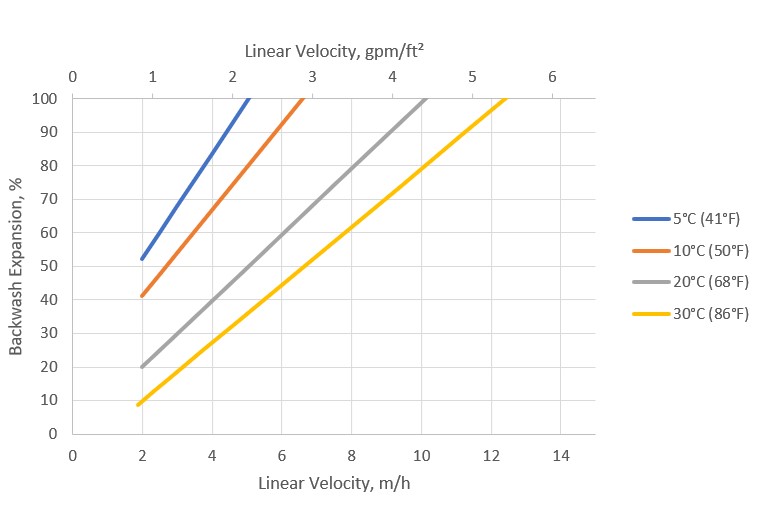
Backwashing:
- During the backwashing process, the resin bed should expand in volume between 50% and 70% for at least 10 to 15 minutes for both resins. This operation aims to free all particulate matter, clean the bed of bubbles and voids, and reclassify the resin spheres to ensure minimum flow resistance. When the resin is first put into service, approximately 30 minutes of expansion is sufficient to properly classify the bed. Bed expansion increases with flow rate and decreases with fluid temperature. It is important to be careful to avoid resin loss from the top of the column due to over-expansion of the bed.
These hydraulic characteristics are fundamental to the design and efficient operation of treatment systems using these resins. Correct pressure drop management and proper backflushing procedures are essential to maintain the efficiency of the ion exchange process, thus ensuring the longevity and optimum performance of the resin.
Anion exchange resins (anionic)
Each of these resins offers unique characteristics that make them suitable for specific applications, ensuring efficiency and reliability in water treatment and demineralization processes.
Anionic resin. Strong base derive their functionality from quaternary ammonium exchange sites. The two main groups of strong base anionic resins are Type 1 and Type 2, depending on the type of amine used during the chemical activation process.
Type 1 resins are suitable for total anion removal in all waters, they should be used in waters with high alkalinity and high silicon content.
Type 2 resins also exhibit removal of all anions, but may be less effective in removing silicon and carbon dioxide from waters where these weak acids constitute more than 30% of the total anions. This type of resins are frequently used in water softeners or water softeners.
They are used in deionization columns in demineralizers. Removes anions from water and requires a large amount of regenerant, commonly soda (hydroxidosodium hydroxide – NaOH).
Weak base anionic resins contain the polyamine functional group, which acts as an acid absorber, removing strong acids from the cation effluent stream. These resins should be used in waters with high sulfate or chloride levels, or where alkalinity and silicon removal is required.
The weak base anionic resin is very efficient, requiring less NaOH soda for regeneration. They cannot be used at high pH and may suffer from oxidation or fouling.